Today, over 4.5 billion people use the internet, and 3.8 billion are active on social media. This shows how social media is a place where narcissistic behavior thrives1. It highlights how social media affects our minds, especially with narcissism and self-promotion.
Sites like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter let users create perfect online versions of themselves. These platforms are full of chances for sharing achievements and personal info1. This makes it easy for narcissistic traits to grow.
Studies link narcissism and social media use closely. People with narcissistic traits often spend more time on social media. And using social media a lot can make narcissistic traits worse1. This relationship makes us wonder about the effects of our online actions on our minds.

The effects of the digital ego are big. As social media changes, we need to know how it changes us. Understanding how narcissism and social media interact helps us better understand our digital lives.
Key Takeaways
- Over 4.5 billion people use the internet globally
- Social media provides a platform for narcissistic behavior
- There’s a reciprocal relationship between narcissism and social media use
- Popular platforms include Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter
- Social media allows users to craft ideal online personas
- Understanding this relationship is crucial for digital well-being
Understanding Narcissism in the Digital Age
In today’s world, social media and online personas have changed how we see narcissism. I’ve seen more people seeking attention and the influencer culture growing. This mix often makes it hard to tell where healthy self-promotion ends and excessive self-love begins.
Definition and Origins of Narcissism
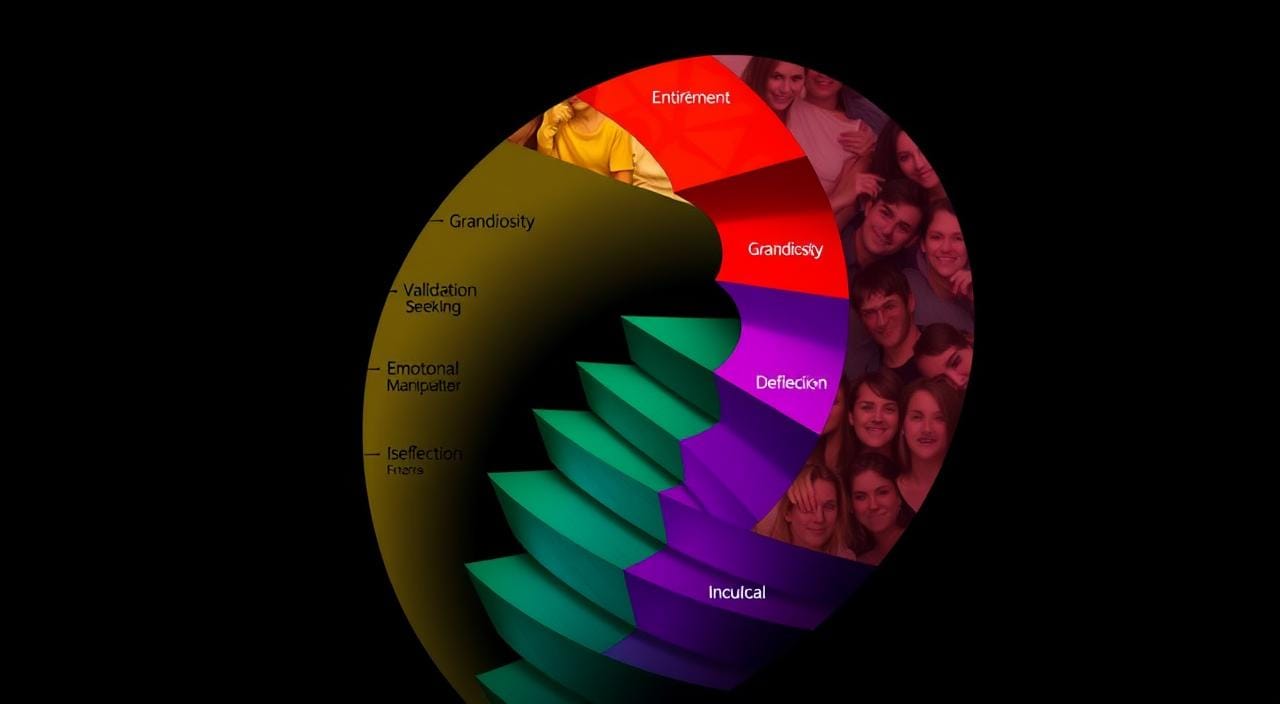
Narcissism comes from the story of Narcissus, a man who fell in love with his own reflection. In psychology, it’s about thinking and acting very self-centered. About 10% of people in their 20s might have some narcissistic traits2. This is worrying, especially since young adults who use social media a lot might become more narcissistic2.
Types of Narcissism
Narcissism isn’t just one thing. There are grandiose and vulnerable types. Grandiose narcissists are outgoing, full of confidence and charm. Vulnerable narcissists are more sensitive and often anxious. Research shows a link between grandiose narcissism and using Facebook too much, with a score of 0.13 to 0.323.
The Rise of Narcissism in Modern Society
The digital age has made narcissistic traits more common. With billions of people on social media, there are many ways to show off. A study found that narcissism in college students went up a lot from 1982 to 20062. People who posted lots of photos and selfies on social media became 25% more narcissistic2.
As we live in this digital world, it’s important to see how our online actions affect us and our relationships. It’s easy to cross the line from healthy self-expression to narcissism, especially in influencer culture and online personas.
The Evolution of Social Media Platforms
Social media has changed how we connect and show ourselves online. These online communities let us build our online identity and seek likes for validation. Today, over 4.5 billion people use the internet, with 3.8 billion active on social media.
Social media keeps changing, offering new ways to interact and share. Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube, and WhatsApp lead the way, each fitting into our digital lives differently. This shows our growing need for online connections and managing our digital image.
Studies reveal how social media affects people differently. Girls use it more than boys, with 43% spending an hour daily by age 15, compared to 31% of boys4. This gap might affect how they act and present themselves online.
The rise of social media has changed how we seek approval and manage our self-image. Not getting enough likes can make people post more, feel distressed, or act aggressively online. This shows how complex our online identity and the validation we seek are.
“Social media is not just a tool; it’s become an integral part of our identity and how we perceive ourselves in relation to others.”
As social media grows, so do our behaviours and what we expect. Research links vulnerable narcissism to spending more time online, posting often, and worrying about likes and comments5. This highlights how our personality affects our digital lives.
Narcissism and Social Media: A Complex Relationship
Social media has become a place where people seek attention and promote themselves. Studies link narcissism with social media use, showing how personality traits affect online actions6.
Self-enhancement Model
People with narcissistic traits use social media to make themselves look better. Research shows that those deeply invested in their online image tend to promote themselves more7. This can make them feel more important and entitled.
Fit Model
Social media meets the needs of narcissistic individuals, offering a perfect space for validation. Studies show narcissism affects how people promote themselves on Instagram6. These platforms let them create a perfect online image.
Trait Model
The trait model looks at how narcissism shows in social media use. People with narcissistic traits often have trouble keeping relationships and may end up alone8. On social media, this can mean acting selfish and not accepting criticism, which can hurt their careers.
Not all social media users become narcissistic, though. Narcissism is a complex trait influenced by many factors, not just social media7. Being aware of oneself and understanding others can reduce the negative effects of social media on narcissism and help build real connections.
The Impact of Different Social Media Platforms on Narcissistic Behaviors
Social media platforms change how we interact online and affect narcissistic behaviors in different ways. Let’s examine how various platforms shape our online identities.
Twitter and Textual-based Platforms
Twitter draws in users who love to share their thoughts. Those high in “superiority” feelings often pick Twitter for its text format. It’s great for quick, clever comments and showing off one’s smarts or achievements.
Facebook and Visual-based Platforms
Platforms like Facebook and Instagram attract those with “exhibitionism” traits. They’re perfect for selfie lovers and those who enjoy showing off. A 2018 study found that posting lots of photos and selfies can boost narcissistic traits by 25%9.
Instagram and Snapchat, with over 2.3 billion users, let people edit their photos. This helps narcissists show off what they think is perfect and unique9. Men tend to show more narcissistic traits through selfies than women, showing gender differences online10.
On these visual platforms, social comparison is huge. People often compare themselves to others’ perfect lives. This can make them feel bad or push them to act narcissistic by trying to look perfect online.
Studies show that vulnerable narcissism is linked to using social media in a bad way more than grandiose narcissism5. This shows the complex link between narcissism types and social media.
Gender Differences in Narcissism and Social Media Use
There are interesting differences in how men and women use social media and show narcissistic traits. Research shows men often have higher narcissism levels, with 8% showing narcissistic traits compared to 5% of women11.
Girls tend to spend more time on social media than boys. Women often compare themselves to others online, which can make them feel less happy and more stressed11.
The influencer culture has made these gender differences more noticeable. Female narcissism on social media often shows through being intimidating and taking a lot of selfies. A study found that taking selfies often can make narcissistic traits worse over time11.
Using social media actively can make people happier and less sad. But just scrolling through it can make people feel more depressed and lower their self-esteem. This shows how different ways of using social media affect people differently11.
“Social networks serve as crucial platforms for individual social comparisons, significantly influencing self-evaluation processes.”
Creating an online persona is key to these differences. Women with high narcissism use social media a lot, post more, and have more online friends. They’re also more likely to get addicted to social media12.
For those with vulnerable narcissism, getting likes and comments is very important. They compare themselves to others, feel jealous, and get upset by negative feedback12.
A study on teens found that using social media for self-centered and appearance-focused reasons affects narcissism. This is especially true for boys in European countries. It shows how gender, culture, and online behavior mix together in complex ways13.
The Role of Cyberbullying and Cyberstalking
The digital age brings new challenges. Online narcissism fuels cyberbullying and cyberstalking. These behaviors link narcissism to social media use. A study of Chinese college students found covert narcissism positively predicts cyberbullying14.
Narcissism as a Predictor of Online Aggression
Narcissistic traits drive online aggression. People with Dark Triad traits (Machiavellianism, psychopathy, narcissism) show problematic social media use15. Narcissists often engage in self-promotion on social platforms. This attention-seeking behavior can lead to conflicts.

Research shows dark personality traits predict cyberbullying, cybertrolling, and cyberstalking15. Machiavellianism shows positive links with cyberstalking, flaming, and trolling. Psychopathy connects to cyberstalking control and flaming. Narcissism relates to cyberstalking and trolling16.
Personal Cybercrimes as a Mediator
Cybercrimes mediate narcissism and social media use. Hostile attribution bias partly explains the link between covert narcissism and cyberbullying14. This cognitive factor influences aggressive behavior online. Anonymity lets covert narcissists express negative emotions indirectly.
Social comparison drives these behaviors. Narcissists use social media for self-promotion, often through deceptive posts and selfies16. This creates a cycle of attention-seeking and online aggression. Understanding these links can help develop better intervention strategies for cyberbullying prevention.
Social Comparison and Its Effects on Self-Esteem
Social media is where people often compare themselves to others. In Australia, about 90% of young adults use sites like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok17. This means they’re always looking at others’ perfect lives online.
Comparing ourselves to others on social media hurts our self-esteem. Studies show it can lead to feeling bad about ourselves and even depression17. Women are especially affected, using social media in ways that can harm their mental health17.
Wanting likes online makes us keep comparing ourselves. In 2020, people in the U.S. spent about 82 minutes a day on social networks, up from 76 minutes the year before18. This means more chances to feel bad about ourselves by comparing.
“Social media has turned into a virtual stage where we perform our best selves, often at the cost of our authentic experiences.”
Using social media too much can make us feel lonely, anxious, and depressed18. Feeling left out because of what others post can make us think too much, leading to depression18. Our online lives really affect how we feel about ourselves.
The Selfie Phenomenon and Narcissistic Traits
Social media has made selfies a big deal. This trend shows our need to create the perfect online image. It’s a deep dive into how we see ourselves and others.
Exploitativeness and Increased Selfie-Taking
Selfie-taking is closely linked to how we view our bodies. Women focus more on their looks than men19. This affects how we use social media.
Sharing selfies meets our need to show off and seek attention. It’s driven by social pressure, wanting to be noticed, and feeling like we belong19. Taking and sharing selfies has turned into a way to manage ourselves.
Sexualized Self-Portrayal and Its Consequences
Selfies have a big impact on us. A study showed that 55% of people feel posting selfies makes them more narcissistic20. This is especially true for those who score high on narcissism, who tend to post, tag, and comment more.
Interestingly, 52% of teens say social media has made them more confident20. This positive feedback can make us take and share more selfies. It’s a cycle that keeps us seeking attention and shapes our online identities.
The selfie trend is more than just about looking good. It’s a mix of psychology, tech, and social norms. As we move through the digital world, it’s key to see how our online actions affect us and our relationships.
The Reinforcement Cycle: Likes, Validation, and Narcissistic Behavior
Social media has created a powerful cycle through likes and validation. This cycle fuels online narcissism. High social media use often links to higher narcissism, especially grandiose narcissism. This type is marked by feelings of entitlement and superiority21.
Many users chase validation through likes. A 2018 study showed that posting lots of photos and selfies can increase narcissistic traits by 25%21. This behavior gets a boost from algorithms that make certain content go viral.

Narcissists use social media more than others, sharing their achievements and looks. They see social media as a key source of validation, boosting their self-esteem22.
But this cycle of validation can be harmful. Without enough validation, narcissists may feel anxious, depressed, or lonely22. This can make them act out online, causing harm to their mental health.
“The validation and fame from social media are short-lived, lasting only a few seconds or minutes before crashing back down to base level.”
This short-lived validation creates a vicious cycle. Users seek attention and positive feedback online, neglecting real-life connections. This focus on an ideal online image can lead to unrealistic expectations and more competition22.
Narcissistic Rage and Online Aggression
I’ve seen a worrying trend in how people act online, linked to narcissism and aggression. Studies show narcissism can lead to a 21% jump in aggression and an 18% increase in violence23. This link covers various aggressive behaviors, like physical, verbal, and indirect aggression, both online and offline23.
Social media can make narcissistic traits worse, causing more attention-seeking and aggression online24. When narcissists don’t get the attention they want, they often get angry and upset. This anger shows up as aggressive behavior online, aimed at putting others down while keeping their own ego up.
Being anonymous online can make narcissists act more aggressively. They’re more likely to be addicted to social media and bully others online24. This is a big problem because it creates a toxic online space filled with negative social comparisons.
“The internet is a breeding ground for narcissistic rage, where the smallest perceived slight can trigger an avalanche of aggression.”
It’s scary that narcissism and aggression are linked across different groups, like gender, age, and culture23. This shows we need to be more aware and find ways to deal with online narcissism and its bad effects on digital communities.
The Psychological Impact of Social Media on Vulnerable Individuals
Social media deeply affects our mental health, especially for those with online narcissism. By 2023, it’s expected that 4.9 billion people will use social media. This shows how big of a deal it is25.
Stress Hormones and Internet Addiction
Wanting likes can make people feel stressed, similar to being addicted to the internet. Those with online narcissism often need constant praise and get upset by criticism. This makes them check their phones a lot and react strongly to bad comments26. They might even feel bad when they’re not online26.
Effects on Self-Esteem and Mental Health
Comparing ourselves to others on social media can really hurt our self-esteem. Studies show that comparing ourselves online can lead to bad body image and depression, especially in girls25. In 2021, over 40% of high school students felt depressed, and depression and anxiety in young people were rising before COVID-1925.
Taking breaks from social media can really help our mental health. Just an hour off a day can make a big difference26. Setting limits and talking about social media with adults can help young people stay healthy25.
“Social media’s impact on our psyche is a double-edged sword. While it connects us, it can also leave us feeling more isolated than ever.”
Addressing the Narcissism-Social Media Connection
The rise of social media has raised concerns about its effect on narcissistic behaviors. With over 75% of the world’s population using social platforms, it’s vital to look into this issue27. I think we need a comprehensive approach to deal with it.
Teaching healthy social media use is crucial. We should educate people on how their online personas impact real-life relationships. It’s also key to note that narcissistic traits are on the rise in young people27.
Influencer culture greatly influences online behaviour. Studies show a strong link between problematic Facebook use and narcissistic traits27. In fact, grandiose narcissism is linked to spending more time on social media, posting more updates, having more friends, and taking more selfies27.
Social media platforms should rethink their design. Algorithms that boost narcissistic behaviors need to change. For instance, 69% of people in the U.S. use social media, with Facebook leading the way28. These platforms could add features that promote empathy and real connections.
“We must balance self-expression with empathy in our digital interactions.”
Interventions aimed at narcissistic behaviors online are crucial. Research highlights a strong link between global narcissism and social media behaviors like posting selfies and self-promotion28. By tackling these behaviors, we can make the online world healthier.
Remember, social media isn’t inherently bad. It’s about striking a balance and understanding its impact on us. By taking these steps, we can create a more positive digital space for all.
Conclusion
Looking back, we see how social media affects our mental health. Studies link narcissism with social media, especially platforms like Instagram, where we show off6. This online self-image can make us feel stressed and depressed29.
Research shows that too much social media makes us more narcissistic, especially for young adults30. This is linked to posting pictures and selfies online, which we do to get likes and approval30. It’s a tough cycle, given that Americans spend over 11 hours a day on media30.
But there’s hope. Setting limits on social media and taking breaks can help manage its effects on our self-esteem29. While we can’t cure narcissism, learning empathy and getting help from therapists can make a difference2930. As we navigate the digital world, focusing on our mental health is key.
FAQ
What is narcissism?
Narcissism is when someone thinks too highly of themselves, always wants attention, and doesn’t care much for others. It comes from an ancient Greek myth and was first seen in psychology by Havelock Ellis in 1898.
What are the different types of narcissism?
There are different kinds of narcissism, like primary, secondary, grandiose, and vulnerable. Grandiose narcissists are outgoing, self-centered, and arrogant. Vulnerable narcissists are shy, sensitive, and worried.
How prevalent is social media use?
Over 4.5 billion people use the internet now, and 3.8 billion are on social media. Social media use went up by 9.2% last year. People use it to connect and manage how others see them.
What theoretical models explain the relationship between narcissism and social media use?
Three models help us understand how narcissism and social media connect. The self-enhancement model says narcissists use social media to boost their image. The fit model suggests social media meets their needs. The trait model looks at how narcissistic traits show up in social media actions.
How do different social media platforms relate to narcissistic behaviors?
Text-based platforms like Twitter attract narcissists more. But, using Facebook and visual platforms can make narcissistic traits worse over time.
Are there gender differences in narcissism and social media use?
Men tend to be more narcissistic than women. But, girls and women use social media more and often compare themselves online. This can make them less happy and lead to emotional problems.
How do cyberbullying and cyberstalking relate to narcissism and social media use?
Cyberbullying and cyberstalking link narcissism to social media. Narcissists use intimidation online. This can lead to more social media use, especially by grandiose narcissists.
How does social comparison on social media affect self-esteem?
Social media makes people compare themselves to others, especially women. This can be aggressive for narcissists. Seeing perfect online lives can lower self-esteem and cause emotional issues, especially in the young.
What is the selfie phenomenon and how is it related to narcissistic traits?
Taking selfies is linked to narcissistic traits, especially in women. It can show aggression and a bad self-image. Getting likes can make this behavior worse, hurting vulnerable narcissists.
How do likes and validation on social media relate to narcissistic behavior?
Likes and validation on social media feed narcissistic traits. For vulnerable narcissists, getting likes is key. Not getting enough can make them post more, be more aggressive, and harm their mental health.
What is narcissistic rage and how does it manifest online?
Not getting social approval online can make narcissistic rage happen. This can lead to posting more, feeling distressed, and hurting self-esteem. This rage can be aggressive online, trying to shame others to boost the self-image.
How does social media use affect vulnerable individuals psychologically?
Using social media can raise stress hormones, like in internet addiction. This can hurt health and mental well-being. For those with narcissistic traits, social media can worsen self-esteem and mental health issues.
How can we address the relationship between narcissism and social media?
We need a complex plan to deal with narcissism and social media. This could include teaching about healthy social media use, improving digital skills, and targeting narcissistic behaviors online. Social media platforms should think about their design to reduce narcissistic traits.
Source Links
- The relationship between social media use and narcissism | 2020, Volume 5 – Issue 1-2 – https://www.journaltxdbu.com/full-text/44
- Social Media Narcissism: Are the Apps Creating Narcissists? – https://www.newportinstitute.com/resources/mental-health/social-media-narcissism/
- Narcissism and problematic social media use: A systematic literature review – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7244927/
- Narcissism and Social Media: Should We Be Afraid? – https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/digital-world-real-world/201909/narcissism-and-social-media-should-we-be-afraid
- Social Media Use and Vulnerable Narcissism: The Differential Roles of Oversensitivity and Egocentricity – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8431185/
- Narcissism and Social Media: The Role of Communal Narcissism – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8508105/
- The Narcissistic Effect of Social Media: How It’s Changing Us – https://medium.com/geekculture/the-narcissistic-effect-of-social-media-how-its-changing-us-20a14f75e19
- The Narcissistic Personality Disorder Epidemic: Separating Fact from Fiction on Social Media – SMPsychotherapy and Counseling Services – Danbury & Hartford, CT – https://psychotherapyandcounselingservices.com/en/the-narcissistic-personality-disorder-epidemic-separating-fact-from-fiction-on-social-media/
- The link between narcissism and social media – https://www.verdict.co.uk/analyst-comment/narcissism-and-social-media/
- Predicting Narcissism Through Social Media – Office of the Vice President for Research – https://sc.edu/about/offices_and_divisions/research/news_and_pubs/caravel/archive/2021_spring/2021_narcissism.php
- Frontiers | Vulnerable Narcissism in Social Networking Sites: The Role of Upward and Downward Social Comparisons – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.711909/full
- Social Media Use and Vulnerable Narcissism: The Differential Roles of Oversensitivity and Egocentricity – https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/17/9172
- The use of social media as a two-way mirror for narcissistic adolescents from Austria, Belgium, South-Korea, and Spain – https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0272868
- The Effects of Covert Narcissism on Cyberbullying | PRBM – https://www.dovepress.com/the-effects-of-covert-narcissism-on-chinese-college-students-cyberbull-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-PRBM
- The Dark Tetrad traits and problematic social media use: The mediating role of cyberbullying and cyberstalking – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S019188691830429X
- Dark Personality Traits and Online Behaviors: Portuguese Versions of Cyberstalking, Online Harassment, Flaming and Trolling Scales – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10298694/
- Social comparisons: A potential mechanism linking problematic social media use with depression – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9295248/
- The effects of social comparison orientation on psychological well-being in social networking sites: Serial mediation of perceived social support and self-esteem – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7556555/
- Selfie-engagement on social media: Pathological narcissism, positive expectation, and body objectification – Which is more influential? – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7244909/
- 10_TaylorWickel_selfies.indd – https://www.csus.edu/faculty/m/fred.molitor/docs/selfies and narcissism.pdf
- Narcissism Today: Trend or Troubling Epidemic? – https://www.deseret.com/lifestyle/2024/07/12/how-to-recognize-narcissism-social-media/
- The Nexus Between Social Media and Narcissism – https://narcissisticexposed.com/social-media-and-narcissism/
- The link between narcissism and aggression – https://www.apa.org/pubs/highlights/spotlight/issue-216
- Social media fuels narcissists’ worst desires, making reasoned debate near impossible | Sonia Sodha – https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/nov/07/social-media-fuels-narcissists-worst-desires-making-reasoned-debate-near-impossible
- Social media brings benefits and risks to teens. Psychology can help identify a path forward – https://www.apa.org/monitor/2023/09/protecting-teens-on-social-media
- A Reflection on Narcissism and Social Media — The Irvington Voice – https://ihsvoice.com/2022/05/30/a-reflection-on-narcissism-and-social-media/
- Is Social Media Turning Us Into Narcissists? – https://www.aplaceofhope.com/is-social-media-turning-us-into-narcissists/
- PDF – https://www.jasnh.com/pdf/Vol16-No1-article3.pdf
- Link Between Social Media and Narcissism – https://varietymatters.medium.com/link-between-social-media-and-narcissism-a8d768bf0c43
- Do Narcissism and Social Media Feed Off Each Other? – https://www.mhconn.org/uncategorized/narcissism-social-media-feed-off/